As you know we can great performance benefits from the new .net 4.0 features like Task Parallel Library (TPL), Coordination Data Structures (CDS) and Parallel LINQ (PLINQ). But all of these features revolve around Task Parallelism. Now what about data parallelism? Should I be writing a Parellel.ForEach just to add elements of an integer array?
To provide a tool, for this need, in the toolkit of developer, there has been work going on in Microsoft for sometime. This is called Microsoft Accelerator Project. The whole idea around Accelerator is to provide implicit parallelism for array processing through functional constructs provided through managed wrapper in any .net language.
In this article I would not be discussing about the detailed architecture of Acclerator. I would just be presenting the introduction of this framework so that an application developer might be using it easily using the functional programming constructs provided in the toolkit. In parallel processing world, a vector is a one-dimensional array. We have always been in need to exploit parallel operations in our software. Using accelerator, you would really have the following resulting logical behavior.
var arr3 = arr1 + arr2;
Here arr1 and arr2 may be two numeric arrays. This is evident from above statement that Accelerator is based on SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) architecture of Flynn’s taxonomy.
Target Platforms:
When Accelerator was first introduced, the whole idea was to use the capabilities (large numbers of arithmetic units) of graphics processor for computations even in non-graphic applications to gain huge speed-ups. But after the introduction of multicore machines in general use, it was updated to take advantage of multiple cores. Now the developer has option to use either of graphics processor (GPU) or multiple main cores in the machine.
With Acclerator, we can target the code generation for two platforms. They are as follows:
1.DX9: To run the computation on GPU. When we specify this target then the code is JIT compiled into pixel shader code and pushed to GPU for processing. After computation, the result is pushed back to the CPU and the result is available for the main program.
2.X64MulticoreTarget: To run the computation on a multicore CPU (only 64 bits).
How it works?
Accelerator uses delayed processing (Lazy computations) to perform its computations. It keeps on adding all the operations in the form of a graph. As the framework receives instructions to execute the computations, it translates the graph based on the platform selected (DX9 or X64MulticoreTarget). It sends the generated code the target and receives result where it gets executed. These results are then provided to the calling program.
This is the same process as in LINQ. It maintains the operations and operands in the form of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG) in order to execute them later on. This DAG is called Expression Graph. After computation the Data Parallel object is converted to System.Object object (Array or Bitmap).
The idea is load your arrays in DataParallelArray objects (discussed later). Perform computations on them. Convert them to System.Object back when the computation is done.
Accelerator Architecture:
ParallelArray:
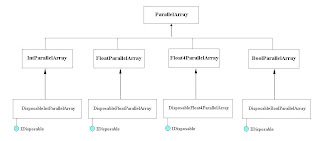
The architecture of accelerator is based on ParallelArray class. This is the base class of 4 classes available. They are IntParallelArray, FloatParallelArray, Float4ParallelArray and BoolParallelArray. They are further specialized with their disposable versions like DisposableIntParallelArray, DisposableFloatParallelArray, DisposableFloat4ParallelArray and DisposableBoolParallelArray.
ParallelArrays:
It is a set of static methods for parallel operations. These operations also include initialization and uninitialization CPU and GPU accelerator. Some of these operations are also available through the overloaded operators for array by Accelerator.
Exception:
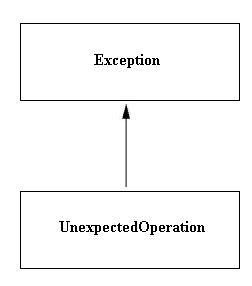
The framework also supports exceptions. Currently only UnexpectedOperation exception is supported.
Using Accelerator in .net Applications:
To use accelerator in .net projects, following steps should be followed:
•Install Accelerator. The latest download (msi) can be obtained from the following Microsoft Connect page. https://connect.microsoft.com/acceleratorv2
•Add a reference of Microsoft.Accelerator.dll in your project. The library should be available in the installation directory of Microsoft Accelerator
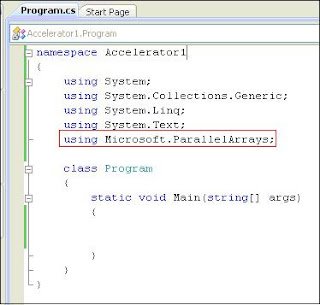
•Add Microsoft.ParallelArrays namespace to the desired namespace. It includes all the accelerator types to write data parallel operations.
•Copy Accelerator.dll from the installation folder of Microsoft Acclerator v2 (…\Microsoft\Accelerator v2\bin\x86\Release) to the application folder. Since I am running in on an x86 machine, I have copied x86 version of the dll. You might use x64 one for a 64-bit machine.
Operations supported:
•Element Wise operations
In this kind of operation, an operation is applied between corresponding elements of an array. The dimensions of the operands should be same for this kind of operations. In the following example, we have added the elements of two float arrays. The results are available in result float array. As expected, the result is {2.0f, 4.0f, 6.0f, 8.0f, 10.0f}.
float[] arr1 = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f, 5.0f };
float[] arr2 = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f, 5.0f };
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_arr2 = new FloatParallelArray(arr2);
var acc_arr3 = ParallelArrays.Add(acc_arr1, acc_arr2);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_arr3);
Since ‘+’ operator is overloaded, we could write the same operation as follows:
var acc_arr3 = acc_arr1 + acc_arr2;
•Reductions (sum, product, min, max etc).
Accelerator supports reduction operations using ParallelArrays. In the following example, we are obtaining sum of all elements of a float array.
float[] arr1 = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f, 5.0f };
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.Sum(acc_arr1);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_result);
•Conversions between Ints and Floats:
Not only we can do operations on arrays, we can also convert between them. In the following example, we are converting an int array to a float one.
int[] arr1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
var acc_arr1 = new IntParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.ToFloatParallelArray(acc_arr1);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_result);
To verify the actual conversion, IDE can also help during debugging.
•Logical operations:
Accelerator may be used for performing various logical operations on operands. These operations might be boolean (Not, AND, OR), comparison (Less than, GreaterThan) and selection operations (Selection). Currently most of these operations are not implemented completely.
float[] arr1 = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f };
float[] arr2 = { 0.0f, 1.0f, 7.0f, 3.0f };
bool[] arr3 = { false, true, false, true };
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_arr2 = new FloatParallelArray(arr2);
var acc_arr3 = new BoolParallelArray(arr3);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.Cond(acc_arr3, acc_arr1, acc_arr2);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_result);
The above code should result in {0.0f, 2.0f, 7.0f, 4.0f} in result. But currently, it has {0.0f, 1.0f, 7.0f, 3.0f} (which is definitely an issue).
•Transformations on data parallel arrays (shift, duplicate):
Some operations require transformation of arrays to be used in an operation. In the following example, we are creating an array. The elements of the result array are the sum of the element in the original array in the specified position and the element before it.
float[] arr1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.Add(ParallelArrays.Shift(acc_arr1, -1), acc_arr1);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_result);
Some operations require transformation of arrays to be used in an operation. In the following example, we are creating an array. The elements of the result array are the sum of the element in the original array in the specified position and the element before it.
This explains that (-1) has shifted each element 1 position to the right keeping the 1st element and truncating the last one.
•Matrix computations:
There are many matrix operations which are directly available in Acclerator. The other operations can be implemented using already existing element wise, transformation and reduction operations available.
In the following example, we are creating the transpose of a matrix.
float[,] arr1 = {
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 }
};
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.Transpose(acc_arr1);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray2D(acc_result);
You can see that instead of using ToArray1D method from target, we have used ToArray2D operation. The result array should be as follows:
{
{ 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2, 2, 2 },
{ 3, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 4, 4, 4, 4 }
};
Application Areas:
The main areas which have potential for extensive use of Accelerator are compression and image processing. These are the areas where there is large number of array processing and matrix manipulation operations.
To provide a tool, for this need, in the toolkit of developer, there has been work going on in Microsoft for sometime. This is called Microsoft Accelerator Project. The whole idea around Accelerator is to provide implicit parallelism for array processing through functional constructs provided through managed wrapper in any .net language.
In this article I would not be discussing about the detailed architecture of Acclerator. I would just be presenting the introduction of this framework so that an application developer might be using it easily using the functional programming constructs provided in the toolkit. In parallel processing world, a vector is a one-dimensional array. We have always been in need to exploit parallel operations in our software. Using accelerator, you would really have the following resulting logical behavior.
var arr3 = arr1 + arr2;
Here arr1 and arr2 may be two numeric arrays. This is evident from above statement that Accelerator is based on SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) architecture of Flynn’s taxonomy.
Target Platforms:
When Accelerator was first introduced, the whole idea was to use the capabilities (large numbers of arithmetic units) of graphics processor for computations even in non-graphic applications to gain huge speed-ups. But after the introduction of multicore machines in general use, it was updated to take advantage of multiple cores. Now the developer has option to use either of graphics processor (GPU) or multiple main cores in the machine.
With Acclerator, we can target the code generation for two platforms. They are as follows:
1.DX9: To run the computation on GPU. When we specify this target then the code is JIT compiled into pixel shader code and pushed to GPU for processing. After computation, the result is pushed back to the CPU and the result is available for the main program.
2.X64MulticoreTarget: To run the computation on a multicore CPU (only 64 bits).
How it works?
Accelerator uses delayed processing (Lazy computations) to perform its computations. It keeps on adding all the operations in the form of a graph. As the framework receives instructions to execute the computations, it translates the graph based on the platform selected (DX9 or X64MulticoreTarget). It sends the generated code the target and receives result where it gets executed. These results are then provided to the calling program.
This is the same process as in LINQ. It maintains the operations and operands in the form of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG) in order to execute them later on. This DAG is called Expression Graph. After computation the Data Parallel object is converted to System.Object object (Array or Bitmap).
The idea is load your arrays in DataParallelArray objects (discussed later). Perform computations on them. Convert them to System.Object back when the computation is done.
Accelerator Architecture:
ParallelArray:
The architecture of accelerator is based on ParallelArray class. This is the base class of 4 classes available. They are IntParallelArray, FloatParallelArray, Float4ParallelArray and BoolParallelArray. They are further specialized with their disposable versions like DisposableIntParallelArray, DisposableFloatParallelArray, DisposableFloat4ParallelArray and DisposableBoolParallelArray.
ParallelArrays:
It is a set of static methods for parallel operations. These operations also include initialization and uninitialization CPU and GPU accelerator. Some of these operations are also available through the overloaded operators for array by Accelerator.
Exception:
The framework also supports exceptions. Currently only UnexpectedOperation exception is supported.
Using Accelerator in .net Applications:
To use accelerator in .net projects, following steps should be followed:
•Install Accelerator. The latest download (msi) can be obtained from the following Microsoft Connect page. https://connect.microsoft.com/acceleratorv2
•Add a reference of Microsoft.Accelerator.dll in your project. The library should be available in the installation directory of Microsoft Accelerator
•Add Microsoft.ParallelArrays namespace to the desired namespace. It includes all the accelerator types to write data parallel operations.
•Copy Accelerator.dll from the installation folder of Microsoft Acclerator v2 (…\Microsoft\Accelerator v2\bin\x86\Release) to the application folder. Since I am running in on an x86 machine, I have copied x86 version of the dll. You might use x64 one for a 64-bit machine.
Operations supported:
•Element Wise operations
In this kind of operation, an operation is applied between corresponding elements of an array. The dimensions of the operands should be same for this kind of operations. In the following example, we have added the elements of two float arrays. The results are available in result float array. As expected, the result is {2.0f, 4.0f, 6.0f, 8.0f, 10.0f}.
float[] arr1 = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f, 5.0f };
float[] arr2 = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f, 5.0f };
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_arr2 = new FloatParallelArray(arr2);
var acc_arr3 = ParallelArrays.Add(acc_arr1, acc_arr2);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_arr3);
Since ‘+’ operator is overloaded, we could write the same operation as follows:
var acc_arr3 = acc_arr1 + acc_arr2;
•Reductions (sum, product, min, max etc).
Accelerator supports reduction operations using ParallelArrays. In the following example, we are obtaining sum of all elements of a float array.
float[] arr1 = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f, 5.0f };
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.Sum(acc_arr1);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_result);
•Conversions between Ints and Floats:
Not only we can do operations on arrays, we can also convert between them. In the following example, we are converting an int array to a float one.
int[] arr1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
var acc_arr1 = new IntParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.ToFloatParallelArray(acc_arr1);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_result);
To verify the actual conversion, IDE can also help during debugging.
•Logical operations:
Accelerator may be used for performing various logical operations on operands. These operations might be boolean (Not, AND, OR), comparison (Less than, GreaterThan) and selection operations (Selection). Currently most of these operations are not implemented completely.
float[] arr1 = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f };
float[] arr2 = { 0.0f, 1.0f, 7.0f, 3.0f };
bool[] arr3 = { false, true, false, true };
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_arr2 = new FloatParallelArray(arr2);
var acc_arr3 = new BoolParallelArray(arr3);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.Cond(acc_arr3, acc_arr1, acc_arr2);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_result);
The above code should result in {0.0f, 2.0f, 7.0f, 4.0f} in result. But currently, it has {0.0f, 1.0f, 7.0f, 3.0f} (which is definitely an issue).
•Transformations on data parallel arrays (shift, duplicate):
Some operations require transformation of arrays to be used in an operation. In the following example, we are creating an array. The elements of the result array are the sum of the element in the original array in the specified position and the element before it.
float[] arr1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.Add(ParallelArrays.Shift(acc_arr1, -1), acc_arr1);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray1D(acc_result);
Some operations require transformation of arrays to be used in an operation. In the following example, we are creating an array. The elements of the result array are the sum of the element in the original array in the specified position and the element before it.
This explains that (-1) has shifted each element 1 position to the right keeping the 1st element and truncating the last one.
•Matrix computations:
There are many matrix operations which are directly available in Acclerator. The other operations can be implemented using already existing element wise, transformation and reduction operations available.
In the following example, we are creating the transpose of a matrix.
float[,] arr1 = {
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 }
};
var acc_arr1 = new FloatParallelArray(arr1);
var acc_result = ParallelArrays.Transpose(acc_arr1);
var target = new DX9Target();
var result = target.ToArray2D(acc_result);
You can see that instead of using ToArray1D method from target, we have used ToArray2D operation. The result array should be as follows:
{
{ 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2, 2, 2 },
{ 3, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 4, 4, 4, 4 }
};
Application Areas:
The main areas which have potential for extensive use of Accelerator are compression and image processing. These are the areas where there is large number of array processing and matrix manipulation operations.