| NEWS |
Friday, March 26, 2010
Features of .Net 2.0, 3.0, 3.5 and 4.0
CLR VERSION 2.0
FRMEWORK LIBRARIES : .NETfx 2.0
LANGUAGE : C# 2.0 VB 8.0
• A new hosting API for native applications wishing to host an instance of the .NET runtime
• Full 64-bit support for both the x64 and the IA64 hardware platforms.
• Language support for Generics built directly into the .NET CLR.
• Many additional and improved ASP.NET web controls.
• New data controls with declarative data binding.
• New personalization features for ASP.NET, such as support for themes, skins and webparts.
.NET 3.0
CLR VERSION 2.0
FRMEWORK LIBRARIES : .NETfx 3.0
LANGUAGE : C# 2.0 VB 8.0
• Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF), formerly code-named Avalon; a new user interface subsystem and API based on XML and vector graphics, which will make use of 3D computer graphics hardware and Direct3D technologies.
• Windows Communication Foundation (WCF), formerly code-named Indigo; a service-oriented messaging system which allows programs to interoperate locally or remotely similar to web services.
• Windows Workflow Foundation (WWF) allows for building of task automation and integrated transactions using workflows.
• Windows CardSpace (WCS), formerly code-named InfoCard; a software component which securely stores a person's digital identities and provides a unified interface for choosing the identity for a particular transaction, such as logging in to a website.
.NET 3.5
• CLR VERSION 2.0
• FRMEWORK LIBRARIES : .NETfx 3.5
• LANGUAGE : C# 3.0 VB 9.0
.NET 2.0 contains CLR.WINFORMS,ASPNET
.NET 3.0 contains complete .net 2.o and WCF,WPF,WF,CARD SPACE
.NET 3.5 contains complete .net 3.0 and LINQ , AJAX
• langauage integrty query (LINQ): it is microsoft .net framwork component adds data native querying capabilities to .net languages using systnax reminiscent of sql.
.Net 4.0
• Parallel Extensions to improve support for parallel computing, which target multi-core or distributed systems.[29] To this end, they plan to include technologies like PLINQ (Parallel LINQ),[30] a parallel implementation of the LINQ engine, and Task
• Parallel Library, which exposes parallel constructs via method calls.
New Visual Basic and C# language features, such as statement lambdas, implicit line continuations, dynamic dispatch, named parameters, and optional parameters.
• Full support for IronPython, IronRuby, and F#.
• Support for a subset of the .NET Framework and ASP.NET with the "Server Core" variant of Windows Server 2008 R2.
Support for Code Contracts.
• Inclusion of the Oslo modelling platform, along with the M programming language
• Inclusion of new types to work with arbitrary-precision arithmetic (System.Numerics.BigInteger) and complex numbers (System.Numerics.Complex)
Read More
Thursday, March 25, 2010
Microsoft Azure platform overview

The Windows Azure platform is a set of cloud computing services that can be used together or independently that enable:
- - Developers use existing skills and familiar tools to develop cloud applications
- - ISVs and System Integrators rapidly reach market and pay as you go
- - IT Managers gain access to a new set of resources without adding complexity
- - Businesses of all sizes to quickly respond as business needs change
Windows Azure provides developers with on-demand compute and storage to host, scale, and manage Web applications on the Internet through Microsoft data centers. Azure goes beyond what other providers, such as Rackspace's Mosso or Amazon's EC2, offer. First, it will be available with a complete suite of tools and technologies for building your next big cloud application. Second, the Azure platform's goal is to support all developers and their choice of IDE, language, and technology; meaning that you can use your favorite tool for all kinds of development as well as Python, PHP, Ruby, Eclipse and so on. It supports popular standards and protocols including SOAP, REST, and XML. Using the Windows Azure tools, developers can build, debug, and deploy to Windows Azure directly from their existing development environment.

Read More..
"Azure" is project name from Microsoft for Cloud Computing. They are going to introduce this from the upcoming version of .NET Framework 4.0. It might make a dramatic changes in the existing Web applications.
Through Cloud computing Microsoft targets for platform independency in their applications.
That is Each web can communicate to any other servers directly.
Advantages for ASP.NET applications:
Following are the advantages of ASP.NET applications by implementing Cloud computing.
1) Cost cutting - Both the small & large scall organizations can implement this.
2) More storage for Data.
3) Mobilitiy of Data - Data can be moved to any kind of servers(e.g Data can easily moved to Unix based machine from Windows).
4) More advantages on BCP(Disaster recoverty etc) plans
By the implementation of Cloud computing, the Web application will give the same level of performance even the traffic to the site is at the peak.
Disadvantages:
Following jobs will be very hectic by the implementation of Azure.
1) Implementation of session
2) Implementation of authentication
3) System Integration.
4) Migration of existing application.
Some of the
key features
of Windows Azure platform are:Windows Azure provides a scalable and highly available virtualized hosting environment on which you can develop and deploy .NET applications. The environment includes machines and load balancers, so that you can create your own scalable applications.
It provides a storage service that includes support for blobs, tables and queues, which means that you can concentrate your development efforts on your core business logic.
It is bundled with lot more other new tools and technologies to leverage your applications with .NET Services, SQL Services, Live Services and so on.
How many times a year have you seen Microsoft’s sites down? Who doesn’t want to host their apps within Microsoft’s Data Centers which pretty much ensures reliability and low downtime?
Scalability? We will talk about it a bit later.
Downloads
- Windows Azure SDK CTP
- Windows Azure Tools for Microsoft Visual Studio October 2008 CTP
- For more information or related downloads: http://www.azure.com/
Some more downloads might be required depending on what you have got installed in your machine, so the best way to get all working is reading the release notes and find the pre-requisites for your PC. After you have installed these as instructed you will be good go with application development on Azure. You will find new items in the New Project dialog box as Blank Cloud Service, Web and Worker Cloud Service etc. in Visual Studio. Obviously - like any other CTPs - Azure SDK may crash your Visual Studio or PC several times during development, so use them at your own risk.
Wednesday, March 24, 2010
Personal Interview FAQs
Go prepared for this question, as this is the most frequently asked question in the interview. Answer it covering your work experience, educational qualifications and a little information about your family background. Try to focus on key areas of your work while talking about your professional experience. This is an open ended question and can help you in taking the interview in which ever direction you want it to go. You should know where to put a full stop to provoke the desired question from the interviewer.
It should be something like:
Hello, My name is John Wales. I’m from New York and born and brought up in the city. My father is a businessman and my mother is a teacher. I have two siblings, an elder brother and an elder sister, both single. I like reading and extremely fond of fiction.
Why does this role interest you? Or why have you applied for this job?
Keep the focus of the answer to this question on your skills, experience and personal qualities. Link the job requirement to your skills rather than talking about the challenges, career and progression.
Why does this role interest you? Or why have you applied for this job?
Try and convince the interviewer that you are there for an interview not because you were called, but because you are supposed to be there and deserve it. Confidence and poise is all that it takes to persuade the interviewer. It should be something like:
This role was something I always wanted to do. I am confident that I will not just be able to achieve the responsibilities that will be given to me, but also learn from them. It will only make me and my company succeed.
Why do you want to leave your present job or why did you leave your last job?
The reasons for switching the job could be numerous. The best answer to offer for this question is to say, “for better prospects”. Now they can ask you another question, what do you mean by better prospects? To this you can say, better prospects in terms of experience, and exposure.
If you have been made redundant, put your words across very carefully. Your wrong words can give an impression that only you were the one whose position was made redundant, which hardly might be the case. May be you can say something like, “Over last 8 months a lot of restructuring was going on in the company and 40 positions became surplus. One of them was mine but I have learnt a lot during my tenure at XYZ company and I am sure I can add a lot of value to a position like the we are discussing about”.
Avoid answers like “I wanted a change”, “I started disliking my job”, “I got bored” etc. Answer should be something like “I felt I was becoming stagnant there and needed to grow”, “I felt as though I can do much more than I was”.
What is your greatest strength?
Interpret this question as, what is your greatest relevant strength? Or Why should we hire you? Tell them a strength that they want to buy. For this you will need to properly understand the job profile and keep your answer ready. For example, if the job needs you to have convincing answers ready for the any type customer’s questions, you can sell “your presence of mind” or if you are required to change you sector or industry you can offer “your adaptability” as an answer. It is important to keep ready at least 2 examples of the mentioned strength.
Avoid answering this question by bragging about yourself. Try and mention strengths related to work. Avoid native answers like “My hard work is my greatest strength”, or “my weakness becomes my strength”. Ideal answers could be “I can adapt to any situation and work atmosphere”, “I’m very flexible”.
What is your greatest weakness?
Interpret this question as, why shouldn’t we hire you? There 3 ways to tackle this question. Judge the situation and use one of them.
First way: Use your sense of humour. If the interview is proceeding in the light way and you have built up a good rapport with the interviewer, you can get out of it by saying “Icecream”. Accompany it with a right body language.
Second Way: If you have to answer this question seriously, give a weakness which doesn’t relate to the job under discussion. For example, you can say, I have been using a camera since childhood but I still don’t know how to mend it. If it is spoiled, I will need to take it to an expert.
Third way: Understand the requirement of the role under discussion and say that others accuse you of having that weakness but you think that it is important for your work. For example, if the job needs a detailed study and leaving a single step might need you to re-run the whole process say that “My colleagues accuse me of having a too much eye for detail but I have experienced that to do this work you need to go into details rather than cutting corners. I have worked with people following a shorter route and doing the whole exercise again, which I would not prefer to do.”
The interviewer seeks an extremely honest answer to this question. Avoid answers like “My strength is my weakness” or “I have no weakness”. Answers may vary depending on the person. Answers like “I take time to mix with people”, “I tend to argue” etc could be some weakness. Try and mention a weakness which will have an impact on the interviewer.
What is your greatest achievement?
The underlying agenda is to know what personal qualities were required to achieve it. Don’t go back too far to answer this question as this might give an impression that you have not achieved anything since then. Find a relevant answer in the recent past for this question. If you are a fresher and have been a topper of your college or university, you can say that during the interview.
Mention about achievements that happened at work. Something related to the past projects and applications you worked on for which you were rewarded. Mention about an achievement that boosted you at work. An achievement that made you confident something related to a module you worked on or got your company some revenue.
You have stayed for a long time with your last company-Why?
Staying with the same company for too long may be considered as the candidate being un-ambitious. While answering this question you can say, “Yes, I preferred to stay with them all this while because I was regularly adding value to my experience there and I was growing as a professional”.
People in my office were friendly and the work atmosphere was comfortable. My manager was extremely cooperative and understood my personal problems. I think that’s what made me stay there for a long time.
You have switched many jobs-why?
Too much job hopping gives an impression that the candidate is unstable and unreliable but you can put this query to ease by saying that you switched jobs to broaden your experience.
The moment I felt I could not give my 100 % to my work or there were some problems with my work, I felt it was time to leave. If I can’t be dedicated or give my 100 %, it is not fair to the company as they put in their resources
Are you speaking to some other companies? Or how is your job search going on?
This question gives you an opportunity to let the interviewer know that other companies are also interested in hiring you and gives you leverage while negotiating the salary. You can say, Yes, I am in the final round of discussion with two other companies. Approach the interviewer as a “Problem Solver” and not as a “Job Beggar”.
Which companies are you talking to?
You can maintain your integrity by refusing to disclose the names. You can simply say, they haven’t notified these openings so I believe they would not like their names to be revealed. At times, taking the competitor’s names might increase your chances of being hires. Analyze the situation and answer accordingly.
Are you ready to relocate?
You can say, for a right position and right company relocation should not be a problem. Do not close the discussion at the earlier stage by saying “No”.
You do not have all the experience we are seeking for this position.
To answer this question, you again need to analyze the requirements of the role properly and match them to your candidature. If you meet most of the requirements, you can say that you have most of the qualities needed for this role and for the remaining you are always open to learning them. You can follow this up with an example from your last job where you learnt and did things that you didn’t know earlier. Stay confident while answering this question.
An interviewer will rarely ask this question as they usually scan your profiles before they call for an interview. If they ask this question, they only want to judge how well can you adapt to negativity. Your answer can be:
“I realize I may not have all the experience. However, we all start from scratch. And its not about how much I know, its about how much can I learn here. I have a passion to learn and I’m sure I can do it”.
What major problems did you face in your last role?
The agenda of this question is to understand if
• You caused the problem
• Could it have been avoided?
• Your attitude to solve it.
It is safer to mention a problem which was caused by an external party rather than the problems within internal parties. May be you can take an example of the problem caused by a customer, vendor. Discuss what you did to solve the problem. If you took some leadership role also in the whole process, talk about it.
Try not to give a very negative answer. Avoid talking ill about your previous company. Answers like “There were no major problems as such. I wanted a change and a hike” would be acceptable.
New Techniques for Removing Duplicate Rows in SQL Server 2005
SQL Server 2005 has introduced the row_number() function, which provides an alternative means of identifying duplicates. Rewriting the first example, for tables with no primary key, we can now assign a row number to each row in a duplicate group, with a command such as:
DECLARE @duplicateTable4 TABLE (data VARCHAR(20))
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('not duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('second duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('second duplicate row')
SELECT data
, row_number() OVER ( PARTITION BY data ORDER BY data ) AS nr
FROM @duplicateTable4
The result will show:
data nr
-------------------- --------------------
duplicate row 1
duplicate row 2
not duplicate row 1
second duplicate row 1
second duplicate row 2
In the above example, we specify an ordering and partitioning for the row_number() function. Note that the row_number() is a ranking window function, therefore the ORDER BY and the PARTITION BY in the OVER clause are used only to determine the value for the nr column, and they do not affect the row order of the query. Also, while the above is similar to our previous GROUP BY clause, there is a big difference concerning the returned rows. With GROUP BY you must use an aggregate on the columns that are not listed after the GROUP BY. With the OVER clause there is no such restriction, and you can get access to the individual rows in the groups specified by the PARTITION BY clause. This gives us access to the individual duplicate rows, so we can get not only the number of occurrences, but also a sequence number for the individual duplicates. To filter out the duplicate rows only, we could just put the above query into a CTE or a subquery. The CTE approach is as follows:
DECLARE @duplicateTable4 TABLE (data VARCHAR(20))
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('not duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('second duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('second duplicate row')
;
WITH numbered
AS ( SELECT data
, row_number() OVER ( PARTITION BY data ORDER BY data ) AS nr
FROM @duplicateTable4
)
SELECT data
FROM numbered
WHERE nr > 1
This is not really any different from what we could do on SQL Server 2000. However, here comes an absolutely amazing feature in SQL Server 2005 and later: We can refer to, and identify, a duplicate row based on the row_number() column and then, with the above CTE expression, we can use a DELETE statement instead of a SELECT, and directly remove the duplicate entries from our table.
We can demonstrate this technique with the following example:
DECLARE @duplicateTable4 TABLE (data VARCHAR(20))
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('not duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('second duplicate row')
INSERT INTO @duplicateTable4 VALUES ('second duplicate row')
;
WITH numbered
AS ( SELECT data
, row_number() OVER ( PARTITION BY data ORDER BY data ) AS nr
FROM @duplicateTable4
)
DELETE FROM numbered
WHERE nr > 1
This solution will even work with large objects, if you stick to the new large object types introduced in SQL Server 2005: i.e. use VARCHAR(MAX) instead of TEXT, NVARCHAR(MAX) instead of NTEXT, and VARBINARY(MAX) instead of IMAGE. These new types are comparable to the deprecated TEXT, NTEXT and IMAGE, and they have the advantage that you will be able to use them with both DISTINCT and row_number().
I find this last solution, using CTE, ROW_NUMBER() and DELETE, fascinating. Partly because now we can identify rows in a table when there is no other alternative way of doing it, and partly because it is a solution to a problem that should not, in theory, exist at all since production tables will have a unique constraint or a primary key to prevent duplicates getting into the table in the first place.
Tuesday, March 23, 2010
How to call a Web Service from client-side JavaScript using ASP.NET AJAX
Introduction
The ASP.NET AJAX framework provides us with an easy and elegant way to consume Web Services from client-side JavaScript code. In fact, it is even easier to write a simple AJAX enabled Web Service and connect to it from client-side JavaScript than it is to write an article like this one. In this article, I have tried to collect some of my experiences which I hope can be useful for you to get started with using the ASP.NET AJAX technology in general and ASP.NET AJAX enabled Web Services in particular.
Background
Some time ago, I was looking for a possibility to dynamically update some parts of my page without refreshing the rest of it. In fact, I only needed to update some small text fields on my page. Apart from this text, my page had a lot of graphics on it, and it was a bit irritating for users to watch the whole page flashing while those text fields were updated. So, I had to avoid refreshing the graphics on the page while updating my text data. The ASP.NET AJAX technology has shown to be the perfect choice for this purpose. It is possible to use different AJAX techniques to achieve this kind of behaviour, for example: partial page updates, page methods, and Web Service calls. In this article, I will try to cover the Web Service approach.
Installing ASP.NET AJAX
Well, first of all, to get started, you will have to install the ASP.NET AJAX framework. You can do the first step by visiting AJAX: The Official Microsoft ASP.NET 2.0 Site. There, you can find links and pretty good instructions on how to install and get started with ASP.NET AJAX. I am using ASP.NET AJAX version 1.0 while writing this article.
Creating an AJAX Enabled Web Service
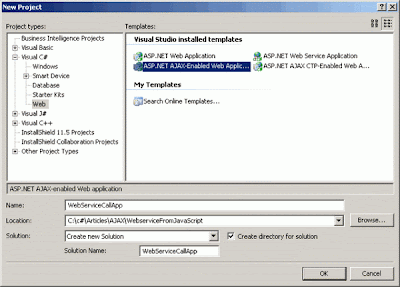
Let us assume that you managed to install the ASP.NET AJAX framework. We can now start with creating a new AJAX enabled Web application:
What we need now is the AJAX enabled Web Service. Let us add a new Web Service called MySampleService to the project:
In order to AJAX enable it, we will have to add the following attribute to the Web Service declaration part:
[System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptService()]When this is done, our Web Service is ready to respond to client-side JavaScript calls. One more thing has to be done here: we need the Web Method that we will call from client-side JavaScript. Let us define it like this:
[WebMethod]
public string GetServerResponse(string callerName)
{
if(callerName== string.Empty)
throw new Exception("Web Service Exception: invalid argument");
return string.Format("Service responded to {0} at {1}",
callerName, DateTime.Now.ToString());
}Configuring the ASP.NET Application
The ASP.NET application's web.config file also has to be modified in order to enable Web Service calls from client-side JavaScript code.
This modification is made for you by Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 if you are using the ASP.NET AJAX template. Here is an example of what can be inserted into the httpHandlers section of your web.config file:
<configuration>
...
<system.web>
...
<httpHandlers>
<remove verb="*" path="*.asmx"/>
<add verb="*" path="*.asmx" validate="false"
type="System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptHandlerFactory,
System.Web.Extensions, Version=1.0.61025.0,
Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35"/>
...
</httpHandlers>
...
</system.web>
...
<configuration>Making Client-side JavaScript Code
Let us take a look at the default.aspx file that was automatically created in our project (if it was not - then you will have to add one manually). First, we have to make sure that we have one and only one instance of the ScriptManager object on our page:
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<asp:ScriptManager ID="ScriptManager1" runat="server">
</asp:ScriptManager>
<div></div>
</form>
</body>Then, we have to add a Services collection to our ScriptManager object, add a ServiceReference to the Services collection, and specify the Path to the desired service. The result might look like this:
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<asp:ScriptManager ID="ScriptManager1" runat="server">
<Services>
<asp:ServiceReference Path="~/WebServices/MySampleService.asmx" />
</Services>
</asp:ScriptManager>
<div></div>
</form>
</body>or like this, if you prefer to do it directly in your code-behind file:
ScriptManager1.Services.Add(new ServiceReference("~/WebServices/MyWebService.asmx"));Now, we need some client-side functions, a button to trigger the Web Service request, and a text box to provide the input for the Web Service:
SendRequest- this function will send an asynchronous request to the Web ServiceOnComplete- this function will receive the result from the Web ServiceOnError- this function will be triggered if an error occurs while executing the Web ServiceOnTimeOut- this function will be triggered if the Web Service will not respondMyTextBox- the ext box with the input for the Web ServiceRequestButton- the button that triggers theSendRequestfunction
The result might look like this:
<head runat="server">
<title>Web Service call from client-side JavaScript</title>
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
function SendRequest()
{
MySampleService.GetServerResponse(form1.MyTextBox.value, OnComplete, OnError,
OnTimeOut);
}
function OnComplete(arg)
{
alert(arg);
}
function OnTimeOut(arg)
{
alert("timeOut has occured");
}
function OnError(arg)
{
alert("error has occured: " + arg._message);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<asp:ScriptManager ID="ScriptManager1" runat="server">
<Services>
<asp:ServiceReference Path="~/WebServices/MySampleService.asmx" />
</Services>
</asp:ScriptManager>
<div>
<input type="text" value="" id="MyTextBox" />
<input type="button" value="Send Request to the Web Service"
id="RequestButton" onclick="return SendRequest()" />
</div>
</form>
</body>This is basically it. You have a functioning client-side JavaScript code that calls a server-side Web Service and treats the returned response. If we supply an empty input value to the GetServerResponse method of MySampleService, then as expected, it will throw an exception. This exception will be caught by the OnError function in the client-side JavaScript:
Conclusion
The described client-to-server communication model where the client-side JavaScript code invokes the Web Service methods provides us with a lot of flexibility to extend our website functionality. At the same time, the traffic is minimal: we send only the input data required by the Web Method, and we receive only the return value from the method being invoked.
Silverlight Interview Questions
Explain Silverlight architecture.
Silver light is a plug-in used for different platforms and
browsers. It is designed for offering media experiences based on .net platform.
Silver light offers a programming environment that is highly adaptable, and
offers support for Ajax, Ruby, and Python etc. It can well be integrated with
the web applications which are already exist.
Designers can work together to create high end silver light
tools for the web using Visual Studio along with Expression Studio. To enable
the users to get high level satisfaction from the tools they use, Microsoft has
been emphasized UX, user experience. UX is the collection of the interactive
points for the user.
The Silverlight architecture has three vital components. They
are described below.
1. Core Presentation Framework: This
framework includes the components, services pertaining to UI including input,
light weight UI controls for use with a web application, media playback, data
binding, vector graphics, text, animation, images for presenting various
features. It includes Extensible Application Markup Language for layout
specification.
2. .NET Framework for Silverlilght: Being a
sub set of .NET framework, it contains the components and libraries. Data
integration, extensible windows controls, networking, base class libraries,
garbage collection, and Common Language Runtime are also included. When
Silverlight Libraries are utilized in applications, all the libraries are
packed with the application and downloaded to the browser. The libraries
include new UI controls, XLINQ, Syndication (RSS/Atom), XML serialization, and
Dynamic Language Runtime (DLR).
3. Installer and Updater: It is a control
for simplifying the installation process for the first-time users. And
subsequently provides automatic updates.
Difference between WPF and Silverlight
In terms of features and functionality, Silver light is a sub
set of Windows Presentation Foundation.
Silver light is for developing rich internet applications.
While WPF is used for developing enhanced graphics applications for desktop
platform.
WPF uses XAML for hosting the user interface for web
applications.
What are the limitations of using external fonts in
Silverlight?
One of the major challenges is to use a downloader and some
of the SetFontSource methods on a TextBlock to perform it.
Using SilverLight 2, TextBlock can be used as follows:
<TextBlock x:Name="Header" FontFamily="timheuer.ttf#Tim
Heuer Normal" />
<TextBlock x:Name="ItemText" FontFamily="timheuer.ttf#Tim Heuer Normal"
/>
Describe how to perform Event handling in silver light
Event handling is performed in two event cases – Input events
and Non-input events.
Input Events: The hosting browser for Silver
Light plug-in handles the input events input stimulus, as SilverLight works
within the hosting browser plug-in architecture. The event is sent to
SilverLight plug-in through the browser. Later the event is raised in the
SilverLight Object Model.
Non-Input Events: These events report a
change state of a particular object. For instance, progress of initiated
actions by the web client. Certain non-input events provide information of
objects as a framework level for lifetime. An example of such event is
FreameworkElementLoaded event.
Explain how to add the reference of a Class library project
in Silverlight application project
The following is the process for adding the reference library
project:
After defining business object classes in another project –
Right click on the SilverLight project root
Choose Add->Existing Item
Navigate through the source code file and select it
Click on the arrow (little) towards the right of the Add
button. Later select Add as link.
Repeat the process for adding all files to your SilverLight
project.
What is Silverlight.js file? Explain with an example.
Silverlight.js file is a Java Script helper file. It supports
for adding a Silverlight application to a web page through Java Script. It has
a number of methods defined to help with, most importantly the createObject and
createObjectEx. The following are certain notable functions and event handlers
:
-getSilverlight, isBrowserRestartRequired, isInstalled,
onGetSilverlight, onSilverlightInstalled, WaitForInstallCompletion.
The Silverlight.js file is installed along with Silverlight 2
SDK.
Using Visual Studio 2008, one can create a quick sample
project by selecting File->New Project and selecting Silverlight
Application. After clicking OK, select “Automatically generate a test page to
host Silverlight at build time”. Click on OK. Right click on the new project
and add an HTML page.
Copy the Silverlight.js into local project directory. Define
a reference to Silverlight.js like any other Java Script file:
<script type="text/javascript"
src="Silverlight.js"></script>
Select createObject or createObjectEx, for creating Silverlight object. Add the
following for creating createObjectEx:
// createObjectEx, takes a single parameter of all
createObject parameters enclosed in {}
Silverlight.createObjectEx = function(params)
{
var parameters = params;
var html =
Silverlight.createObject(parameters.source, parameters.parentElement,
parameters.id, parameters.properties, parameters.events,
parameters.initParams, parameters.context);
if (parameters.parentElement == null)
{
return html;
}
}
What is a .xap file? Explain with an example.
A .xap file is an application package based on Silverlight
which will be generated when the Silverlight project is built. This file
helpful in creating heavily client based Silverlight applications. A managed
code can be used such as C# or VB and benefited by utilizing the tools.
A .xap file has an application manifest file
(AppManifest.xaml) and the necessary DLL’s needed by the application. A
manifest file looks like:
<Deployment xmlns="http:// "….”
xmlns:x="http://......"
EntryPointAssembly="SilverlightApplication1"
EntryPointType="SilverlightApplication1.App" RuntimeVersion="2.0.30226.2">
<Deployment.Parts>
<AssemblyPart
x:Name="SilverlightApplication1" Source="SilverlightApplication1.dll" />
</Deployment.Parts>
</Deployment>
The <Deployment> node describes the application and it
contains child AssemblyPart nodes. The DLLs are contained in .xap file. The
EntryPointAssembly attribute describes the selected assembly defined below is
the main assembly for the application. And EntryPointType attribute describes
the class that contains within the assembly that is defined in the
EntryPointAssembly attribute. This is the class which is instantiated to
commence the application.
Explain how can Silverlight use ASX files.
An ASX file is an XML file in which media files are specified
in the playlist. Using ASX files in silver is pretty simple. Assign the ‘
source’ property of a MediaElement object to the ASX file name.
The following is an example of ASX file.
<ASX version = "3.0">
<TITLE>MyFirst ASX Application</TITLE>
<ENTRY>
<TITLE>MyVideo</TITLE>
<AUTHOR>MyName</AUTHOR>
<COPYRIGHT>(c)2010 A company name</COPYRIGHT>
<REF HREF = "xbox.wmv" />
</ENTRY>
</ASX>
Later this .asx file need to assigned to the ‘Source’ property of MediaElement
in XAML file.
<MediaElement
.
.
Source=”myasxfile.asx”
.
</MediaElement>
Finally, add event handlers for supporting the MediaElement.
The following functions are used for stopping, pausing and playing events on
CurrentStateChanged event.
function media_stop(sender, args)
{
sender.findName("MediaPlayer").stop();
}
function media_pause(sender, args)
{
sender.findName("MediaPlayer").pause();
}
function media_begin(sender, args)
{
player =
sender.findName("MediaPlayer");
player.play();
}
function media_state_changed(sender, args)
{
// Obtain the text block for displaying
the status
var mediaStateTextBlock =
sender.findName("mediaStateTextBlock");
// Obtain the media state object
var media = sender.findName("MediaPlayer");
mediaStateTextBlock.Text = media.CurrentState;
}
Explain Silverlight application life-cycle
The entry point of Silverlight applications is Silverlight
Application class. It provides various services which is commonly needed by
Silverlight application.
Silverlight lifecycle commences with opening a web page for
hosting Silverlight plug-in. If the plug-in is not available, the web page
prompts to install Silverlight browser plug-in. Later the browser activates the
plug-in and starts downloading application package. This plug-in loads the
Silverlight Common Language Runntime by which application domain for
application is created.
Later, CLR creates an object of Application class followed by
raising the Application Startup Event. There will be only one Application
instance in any Silverlight-based application. Upon starting up the application
instance provides several commonly used services by the application.
What is the role of Silverlight Plugin in the Silverlight
Application Life-Cycle?
The Silverlight plug-in loads the core services of
Silverlight followed by Silverlight Common Language Runtime. CLR creates
domains for applications. The plug-in enables Silverlight for delivering
cross-platform and cross-browser applications as a subset of the .NET framework
and Windows Presentation Foundation. The plug-in loads the core services of
Silverlight that creates application domains.
Explain the purpose of Storyboard.TargetProperty.
Using Storyboard.TargetProperty, the properties of an object
can be assigned with values. The objects are referred by Storyboard.TargetName
attribute. The following snippet illustrates the change of width and color of a
rectangle object.
<Storyboard>
<DoubleAnimation Storyboard.TargetName="MyRectangle"
Storyboard.TargetProperty="Width" From="150" To="275" Duration="0:0:2" />
<ColorAnimation Storyboard.TargetName="MySolidColorBrush"
Storyboard.TargetProperty="Color" From="Green" To="Red" Duration="0:0:2" />
</Storyboard>
Why is XAP important?
Using XAP, Silverlight applications which are heavily client
based can be created by managing code. The managed code, benefits of using the
tools such as Visual Studio 2008 with Silverlight Tools Beta version 2 , are
utilized by using XAP.
How does XAP work?
The .xap file is used for transferring and containing the
assemblies and resources of an application with managed code. This code must be
written within the Silverlight browser plugin.
Once the .xap file is created, the Silverlight 2 plug-in will
download the file and executes in a separate work space.
Explain the use of ClientBin folder in Silverlight.
The ClientBin folder is used for placing .xap file of a
Silverlight application. This folder can be kept anywhere in the web
application.
What is Clipping in Silverlight?
Clipping is a modification to a given image / object based on
the geometry type – like a line, rectangle, ellipse or even a group geometry
objects. The clip property is defined in the UIElement class. An XAML code is
used for an Image object for displaying a geometrical image. The following is
the code snippet for setting the Ellipse properties.
<Image Source="Nature.jpg" Width="350" Height="350">
<Image.Clip>
<EllipseGeometry RadiusX="100" RadiusY="100" Center="200,150"/>
</Image.Clip>
</Image>
What is the parent xaml tag of Silverlight page? Explain its
purposes.
The’UserConrol’ is the parent xaml tag of a Silverlight page.
All other tags are authored under UserControl tag. Developers are given a
facility to implement new custom controls and create re-usable user controls.
This makes the use of XAML file easy for composing a control’s UI and easy to
implement.
The following code snippet resembles the UserControl tag.
<UserControl x:Class="SilverlightApplication2.MainPage"
Width="400" Height="300">
<Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot" Background="Green">
</Grid>
</UserControl>
Explain with example how to change the default page of the
Silverlight application.
The RootVisual property of Application_Startup event in
App.xaml file needs to be set to change the default Silverlight application
page. The following code snippet sets the property.
private void Application_Startup(object sender,
StartupEventArgs strtevntarg)
{
this.RootVisual = new
YourPage();
}
How many xaml files are created When you create a new
project in Silverlight through Visual Studio and what are the uses of those
files?
There are two xaml files are created when a new project in
Silverlight is created through Visual Studio.
1. App.xaml – This file is used for
declaring shared resources like style objects, brushes etc and for handling
global application level event. The following are the default events created in
App.xaml.cs file.
Application_Startup
Application_Exit
Application_UnhandledException
ReportErrorToDOM
2. MainPage.xaml or Page.xaml – This file is
the default page of the Silverlight application at the time of silverlight
application’s execution. This is similar to default.aspx page of ast.net
application.
What are the programming language that can be used to write
the backend of the Silverlight application?
Visual Basic or Visual C# can be used for authoring code for
the backend of the Silverlight application. The backend refers the code behind
the files of Silverlight pages.
Explain how to set Silverlight contents width as 100%.
Usually the UserConrol will be spread full screen. The
contents width and height can also be set by using width and height attributes.
To get 100% width of the screen set width=”auto” and height =”auto”.
Can you provide a list of Layout Management Panels and when
you will use them?
The following are the list of Layout Management Panels:
1. Canvas Panel: Simple layouts use canvas panel and when
there is no requirement of resizing the panel. The controls will overlap each
other at the time of resizing the panel.
2. Stack Panel: This panel is used to group the controls in a
stack either horizontally or vertically. The overlapping of controls will not
occur.
3. Grid Panel: Grid Panel is the most flexible layout for
placing controls in multi rows / columns. It resembles an HTML table.
Explain how to apply style elements in a Silverlight
project?
Application resources utilize the style elements for
supporting the forms. The App.xaml file could be used to contain an application
resource XML construct. Each style’s target type is set to the control that
needs the style.
App.xaml:
<Application.Resource>
<Style x:Key="MyBorder" TargetType="Border">
<setter property="width" value="3">
</style>
Page.xaml:
<Border Style="{StaticResource MyBorder}">
...
</Border>
What are the main features and benefits of Silverlight?
The following are the features of SilverLight:
1. Built in CLR engine is available for delivering a super
high performance execution environment for the browser.
2. Includes rich framework of built-in class library for using with
browser-based applications.
3. Supports WPF UI programming model.
4. Provides a managed HTML DOM API which is used for HTML enabled programs of a
browser using .NET technology.
5. Silverlight supports PHP or Linux environment. Hence does not require
ASP.NET.
6. Permits limited access to file system for applications. An OS native file
dialog box can be used for using any file.
The following are the benefits of Silverlight:
1. Supports highest quality videos
2. Supports cross-platform and cross-browser applications
3. Features are available for developers with Visual Studio for developing
applications very quickly.
4. Most inexpensive way for video streaming over internet at the best possible
quality.
5. Supports third party languages such as Ruby, Python, EcmaScript!
6. Supports remote debugging.
7. Provides copy protection.
When would one use Silverlight instead of ASP.NET AJAX?
Silverlight media experiences and Rich Internet Applications
can be enhanced by the existing ASP.NET AJAX applications. Web applications and
ASP.NET AJAX technologies are integrated in Silverlight. They are complementary
technologies. Silverlight can interact with AJAX applications for both
client-side and server-side. Certain examples are applications mapping, video
playback.
When would a customer use Silverlight instead of Windows
Presentation Foundation (WPF)?
Silverlight is used by customers for broader reach of
interactive media content and browser-based rich interactive, high performance
applications.
The features of WPF such as platform, UI, Media, offline communication,
integration of OS, integration of Office, access to peripherals, supporting
documents etc., are integrated into Silverlight.
Does Silverlight have a System.Console class? Why?
Yes. Silverlight have System.Console class. It is cocooned in
the SecurityCritical attribute. It is so for using for internal uses and making
it useless for remote usage.
Is it possible to load external OTF or TTF in Silverlight?
How
It is possible to load external OTF or TTF in Silverlight.
The process is:
Right click on Silverlight application project folder.
Select “Add->New Item…”.
Browse and select the font and click on OK buton
Select the font and set the grid property Build Action =
“Resource”, and “Copy to Output Directory” = “Copy if newer”:
Use the following syntax in the FontFamily attribute of
XAML file
FontFamily=”[FontFileName]#[FontFriendlyName]”
Example: <TextBlock Text="Hello"
FontFamily="Century.ttf#Century"></TextBlock>
To find the exact font name, double click on the font to
open the font viewer.
What are the properties that have to be initialized for
creating a Silverlight control using createSilverlight()?
The properties ‘source’ and ‘elementID’ are to be
initialized. The ‘source’ attribute can be a ‘.xaml’ file or an ‘.aspx’ file.
The elementID can be a string that identifies the file.
Explain what happens (internally) when a user that doesn’t
have the Silverlight runtime accesses a page that uses Silverlight controls.
Explain the Path instructions in XAML
The <Path> instruction of XAML allows to draw and fill
a path. Various points in the path represents are represented by the Data
attribute. The attribute includes M which means to move to command, moves to a
coordinate and C represents the absolute path. The H represents line to
command.
The following is the code snippet to draw a path:
<Path Data="M 200,40 C 50,90 200,250 200,75 H 480"
Stroke="Black" StrokeThickness="4"/>
Explain the resemblance between CSS and Silverlight,
regarding overlapping objects.
Silverlight content is hosted on the tag. CSS of DIV can be
changed as it is for other HTML documents. The changes can be for absolute
positioning, z-indexing, top and left properties etc.
top:14px;">
What kind of Brushed does Silverlight support?
Silverlight brush objects supports for painting with solid
colors, linear gradients, radical gradients and images.
SolidColorBrush is used to paint a closed object such as
rectangle
LinearGradientBrush - used to paint a linear gradient like
glass, water and other smooth surfaces.
RadialGradientBrush – used to paint a radial gradient which
is a blend together along an axis.
Explain the arguments for the addEventListener() method.
The first argument is an action event like mouseDown, mouseUp
etc. The second argument is a call to a function. The following lines
illustrates the use of addEventListener() method.
function myfunction(x) { alert(x) }
Obj.addEventListener(“mouseDown”, myFunction(‘hello’);
Explain the mouse events that Silverlight currently
supports.
The mouse events that supports silverlight are
LostMouseCapture - occurs when an UI element lost mouse
capture
MouseMove - occurs when the mouse position changes
MouseEnter - occurs when the mouse pointer enters into the bounding area of an
object
MouseLeave - occurs when the mouse pointer leaves the bounding area of an
object
MouseLeftButtonDown - occurs when the left mouse button is down
MouseLeftButtonU - occurs when the left mouse button is up followed by
MouseLeftButtonDown
Difference between MouseLeftButtonDown and MouseLeftButtonUp
in Silverlight.
The difference is the action of the button. Once mouse button
is pressed MouseLeftButtonDown event is invoked and MouseLeftButtonUp event is
invoked after pressing left mouse button down and release it.
What is the function used for removing an event listener?
The method removeEventListener() is used for deleting an
event listener. The parameters for this method are eventName and listener.
How would you implement Drag-and-drop in Silverlight?
Drag and drop in Silverlight can be implemented by using Drag
Drop Manager by using DragSource and DropTarget controls. DragSource makes any
control to be draggable and DropTarget defines a location in the application to
drop the DragSources.
What are the properties of the eventArgs argument when
capturing keyboard events?
The properties of eventArgs are types of keys like shift,
ctrl and mouse actions, mouse pointer coordinates, x coordinate value, y
coordinate value
What is the function used to get a reference to an object
inside the Silverlight control?
What objects support tranformations? What are the transformations that
Silverlight supports for the elements?
Explain the steps needed to be performed in order to create an animation in
XAML
What are the animation types supported by Silverlight?
Explain the concept of KeyFrame. What is the difference between Silverlight and
Flash regarding animations?
Explain how to control animation from JavaScript code.
How could you determine the media position when playing a video in Silverlight?
Explain the ways of accessing the Silverlight control from JavaScript?
What are the three units of information that the Silverlight plug-in exposes to
JavaScript?
How could you modify XAML content from JavaScript?
What are the necessary step that need to be performed in order to download
content from within Silverlight?
What ASP.NET control can embed XAML into ASP.NET pages?
Does Silverlight supports database connectivity? Explain
What is the codec Silverlight supports for HD streaming?
How can IIS improve Silverlight Streaming?
How to create hyperlinks in silverlight(in windows presentation foundation)?
What is SMPTE VC-1?
Managed vs. unmanaged code
- Managed code runs through a runtime which is a software layer that the
application communicates due to which many functions are automatically done. Some of these functions are garbage collecting and exception handling. - A programmer needs to write many common functions in an unmanaged code. So functions like garbage collecting, exception handling, etc have to be handled
explicitly.
Explain - consuming unmanaged DLL functions using PInvoke.
PInvoke = Platform invoke.
Calling a function located in an unmanaged DLL library from .NET framework is called consuming unmanaged DLL function.
When PInvoke calls an unmanaged function,
The DLL containing the function is located and loaded it into memory.
Then the function arguments are pushed into the stake and then the data is marshalled required.
And then the control is transferred to the unmanaged function.
PInvoke throws exceptions generated by the unmanaged function to the managed caller.
Explain how managed code slower than unmanaged code.
Managed code executes under the management of a virtual machine. It is executed by a common language runtime environment rather than directly by the operating system. Tasks such as Exception handling and GC too are handled in the managed code environment. Due to all these reasons, managed code is slower than the unmanaged code.
.Net Internals - See how CLR works
- SystemDomain, SharedDomain, and DefaultDomain
- Object layout and other memory specifics
- Method table layout
- Method dispatching
This article uses the following technologies:
.NET Framework, C#
Since the common language runtime (CLR) will be the premiere infrastructure for building applications in Windows® for some time to come, gaining a deep understanding of it will help you build efficient, industrial-strength applications. In this article, we'll explore CLR internals, including object instance layout, method table layout, method dispatching, interface-based dispatching, and various data structures.

Figure 1 SSCLI Reference
| Item | SSCLI Path |
|---|---|
| AppDomain | \sscli\clr\src\vm\appdomain.hpp |
| AppDomainStringLiteralMap | \sscli\clr\src\vm\stringliteralmap.h |
| BaseDomain | \sscli\clr\src\vm\appdomain.hpp |
| ClassLoader | \sscli\clr\src\vm\clsload.hpp |
| EEClass | \sscli\clr\src\vm\class.h |
| FieldDescs | \sscli\clr\src\vm\field.h |
| GCHeap | \sscli\clr\src\vm\gc.h |
| GlobalStringLiteralMap | \sscli\clr\src\vm\stringliteralmap.h |
| HandleTable | \sscli\clr\src\vm\handletable.h |
| InterfaceVTableMapMgr | \sscli\clr\src\vm\appdomain.hpp |
| Large Object Heap | \sscli\clr\src\vm\gc.h |
| LayoutKind | \sscli\clr\src\bcl\system\runtime\interopservices\layoutkind.cs |
| LoaderHeaps | \sscli\clr\src\inc\utilcode.h |
| MethodDescs | \sscli\clr\src\vm\method.hpp |
| MethodTables | \sscli\clr\src\vm\class.h |
| OBJECTREF | \sscli\clr\src\vm\typehandle.h |
| SecurityContext | \sscli\clr\src\vm\security.h |
| SecurityDescriptor | \sscli\clr\src\vm\security.h |
| SharedDomain | \sscli\clr\src\vm\appdomain.hpp |
| StructLayoutAttribute | \sscli\clr\src\bcl\system\runtime\interopservices\attributes.cs |
| SyncTableEntry | \sscli\clr\src\vm\syncblk.h |
| System namespace | \sscli\clr\src\bcl\system |
| SystemDomain | \sscli\clr\src\vm\appdomain.hpp |
| TypeHandle | \sscli\clr\src\vm\typehandle.h |
.gif)
System Domain
!DumpDomain
System Domain: 793e9d58, LowFrequencyHeap: 793e9dbc,
HighFrequencyHeap: 793e9e14, StubHeap: 793e9e6c,
Assembly: 0015aa68 [mscorlib], ClassLoader: 0015ab40
Shared Domain: 793eb278, LowFrequencyHeap: 793eb2dc,
HighFrequencyHeap: 793eb334, StubHeap: 793eb38c,
Assembly: 0015aa68 [mscorlib], ClassLoader: 0015ab40
Domain 1: 149100, LowFrequencyHeap: 00149164,
HighFrequencyHeap: 001491bc, StubHeap: 00149214,
Name: Sample1.exe, Assembly: 00164938 [Sample1],
ClassLoader: 00164a78

Figure 3 Sample1.exe
using System;
public interface MyInterface1
{
void Method1();
void Method2();
}
public interface MyInterface2
{
void Method2();
void Method3();
}
class MyClass : MyInterface1, MyInterface2
{
public static string str = "MyString";
public static uint ui = 0xAAAAAAAA;
public void Method1() { Console.WriteLine("Method1"); }
public void Method2() { Console.WriteLine("Method2"); }
public virtual void Method3() { Console.WriteLine("Method3"); }
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
MyClass mc = new MyClass();
MyInterface1 mi1 = mc;
MyInterface2 mi2 = mc;
int i = MyClass.str.Length;
uint j = MyClass.ui;
mc.Method1();
mi1.Method1();
mi1.Method2();
mi2.Method2();
mi2.Method3();
mc.Method3();
}
}
Our console program, Sample1.exe, is loaded into an AppDomain which has a name "Sample1.exe." Mscorlib.dll is loaded into the SharedDomain but it is also listed against the SystemDomain as it is the core system library. A HighFrequencyHeap, LowFrequencyHeap, and StubHeap are allocated in each domain. The SystemDomain and the SharedDomain use the same ClassLoader, while the Default AppDomain uses its own.
Figure 2 shows the default Process Heap, JIT Code Heap, GC Heap (for small objects) and Large Object Heap (for objects with size 85000 or more bytes) to illustrate the semantic difference between these and the loader heaps. The just-in-time (JIT) compiler generates x86 instructions and stores them on the JIT Code Heap. GC Heap and Large Object are the garbage-collected heaps on which managed objects are instantiated.

Figure 4 Large Objects and Small Objects
using System;
class SmallClass
{
private byte[] _largeObj;
public SmallClass(int size)
{
_largeObj = new byte[size];
_largeObj[0] = 0xAA;
_largeObj[1] = 0xBB;
_largeObj[2] = 0xCC;
}
public byte[] LargeObj
{
get { return this._largeObj; }
}
}
class SimpleProgram
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SmallClass smallObj = SimpleProgram.Create(84930,10,15,20,25);
return;
}
static SmallClass Create(int size1, int size2, int size3,
int size4, int size5)
{
int objSize = size1 + size2 + size3 + size4 + size5;
SmallClass smallObj = new SmallClass(objSize);
return smallObj;
}
}
Figure 5 shows snapshot of a typical fastcall stack frame stopped at a breakpoint at the "return smallObj;" line inside the Create method. (Fastcall is the .NET calling convention which specifies that arguments to functions are to be passed in registers, when possible, with all other arguments passed on the stack right to left and popped later by the called function.) The value type local variable objSize is inlined within the stack frame. Reference type variables like smallObj are stored as a fixed size (a 4-byte DWORD) on the stack and contain the address of object instances allocated on the normal GC Heap. In traditional C++, this is an object pointer; in the managed world it's an object reference. Nonetheless, it contains the address of an object instance. We'll use the term ObjectInstance for the data structure located at the address pointed to by the object reference.
.gif)
SmallClass obj = new SmallClass()
// Do some work here
lock(obj) { /* Do some synchronized work here */ }
obj.GetHashCode();
.gif)
In this code, smallObj will use zero (no syncblk) as its starting syncblk number. The lock statement causes the CLR to create a syncblk entry and update the object header with the corresponding number. As the C# lock keyword expands to a try-finally that makes use of the Monitor class, a Monitor object is created on the syncblk for synchronization. A call to the GetHashCode method populates the syncblk with the object hash code.

Figure 7 SimpleClass with Instance Variables
class SimpleClass
{
private byte b1 = 1; // 1 byte
private byte b2 = 2; // 1 byte
private byte b3 = 3; // 1 byte
private byte b4 = 4; // 1 byte
private char c1 = 'A'; // 2 bytes
private char c2 = 'B'; // 2 bytes
private short s1 = 11; // 2 bytes
private short s2 = 12; // 2 bytes
private int i1 = 21; // 4 bytes
private long l1 = 31; // 8 bytes
private string str = "MyString"; // 4 bytes (only OBJECTREF)
//Total instance variable size = 28 bytes
static void Main()
{
SimpleClass simpleObj = new SimpleClass();
return;
}
}
Figure 8 shows an example of a SimpleClass object instance in the Visual Studio debugger memory window. We set a breakpoint on the return statement in Figure 7 and used the address of the simpleObj contained in the ECX register to display object instance in the memory window. The first 4-byte block is the syncblk number. As we didn't use the instance in any synchronizing code (or access its HashCode), this is set to 0. The object reference, as stored in the stack variable, points to 4 bytes starting at offset 4. The Byte variables b1, b2, b3, and b4 are all packed side by side. Both of the short variables, s1 and s2, are packed together. The String variable str is a 4-byte OBJECTREF that points to the actual instance of the string located on the GC Heap. String is a special type in that all instances containing the same literal will be made to point to the same instance in a global string table during the assembly loading process. This process is called string interning and is designed to optimize memory usage. As we mentioned previously, in the .NET Framework 1.1, an assembly cannot opt out of this interning process, although future versions of CLR may provide this capability.
.gif)
!DumpHeap -type SimpleClass
Loaded Son of Strike data table version 5 from
"C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v1.1.4322\mscorwks.dll"
Address MT Size
00a8197c 00955124 36
Last good object: 00a819a0
total 1 objects
Statistics:
MT Count TotalSize Class Name
955124 1 36 SimpleClass
The total size of the object is 36 bytes. No matter how large the string is, instances of SimpleClass contain only DWORD OBJECTREF. SimpleClass's instance variables only occupy 28 bytes. The remaining 8 bytes are comprised of the TypeHandle (4 bytes) and the syncblk number (4 bytes). Having found the address of the instance simpleObj, let's dump the contents of this instance using the DumpObj command, as shown here:
!DumpObj 0x00a8197c
Name: SimpleClass
MethodTable 0x00955124
EEClass 0x02ca33b0
Size 36(0x24) bytes
FieldDesc*: 00955064
MT Field Offset Type Attr Value Name
00955124 400000a 4 System.Int64 instance 31 l1
00955124 400000b c CLASS instance 00a819a0 str
<< some fields omitted from the display for brevity >>
00955124 4000003 1e System.Byte instance 3 b3
00955124 4000004 1f System.Byte instance 4 b4
As noted, the default layout generated for classes by the C# compiler is LayoutType.Auto (for structs, LayoutType.Sequential is used); hence the class loader rearranged the instance fields to minimize the padding. We can use ObjSize to dump the graph that includes the space taken up by the instance, str. Here's the output:
!ObjSize 0x00a8197c
sizeof(00a8197c) = 72 ( 0x48) bytes (SimpleClass)
If you subtract the size of the SimpleClass instance (36 bytes) from the overall size of the object graph (72 bytes), you should get the size of the str—that is, 36 bytes. Let's verify this by dumping the str instance. Here's the output:
!DumpObj 0x00a819a0
Name: System.String
MethodTable 0x009742d8
EEClass 0x02c4c6c4
Size 36(0x24) bytes
If you add the size of the string instance str (36 bytes) to the size of SimpleClass instance (36 bytes), you get a total size of 72 bytes, as reported by the ObjSize command.
Figure 9 shows the typical layout of the MethodTable. We'll show some of the important fields of the TypeHandle, but for a more complete list, look at the figure. Let's start with the Base Instance Size as it has direct correlation to the runtime memory profile.
.gif)
!DumpHeap -type MyClass
Address MT Size
00a819ac 009552a0 12
total 1 objects
Statistics:
MT Count TotalSize Class Name
9552a0 1 12 MyClass
.gif)

Figure 11 SOS Dump of MyClass Method Table
!DumpMT -MD 0x9552a0
Entry MethodDesc Return Type Name
0097203b 00972040 String System.Object.ToString()
009720fb 00972100 Boolean System.Object.Equals(Object)
00972113 00972118 I4 System.Object.GetHashCode()
0097207b 00972080 Void System.Object.Finalize()
00955253 00955258 Void MyClass.Method1()
00955263 00955268 Void MyClass.Method2()
00955263 00955268 Void MyClass.Method2()
00955273 00955278 Void MyClass.Method3()
00955283 00955288 Void MyClass..cctor()
00955293 00955298 Void MyClass..ctor()
.gif)
!u 0x00955263
Unmanaged code
00955263 call 003C3538 ;call to the jitted Method2()
00955268 add eax,68040000h ;ignore this and the rest
;as !u thinks it as code
Now let's execute the method and disassemble the same address:
!u 0x00955263
Unmanaged code
00955263 jmp 02C633E8 ;call to the jitted Method2()
00955268 add eax,0E8040000h ;ignore this and the rest
;as !u thinks it as code
Only the first 5 bytes at the address is code; the rest contains data of Method2's MethodDesc. The "!u" command is unaware of this and generates gibberish, so you can ignore anything after the first 5 bytes.
!DumpMD 0x00955268
Method Name : [DEFAULT] [hasThis] Void MyClass.Method2()
MethodTable 9552a0
Module: 164008
mdToken: 06000006
Flags : 400
IL RVA : 00002068
After compilation, MethodDesc looks like this:
!DumpMD 0x00955268
Method Name : [DEFAULT] [hasThis] Void MyClass.Method2()
MethodTable 9552a0
Module: 164008
mdToken: 06000006
Flags : 400
Method VA : 02c633e8
The Flags field in the method descriptor is encoded to contain the information about the type of the method, such as static, instance, interface method, or COM implementation.
mi1.Method1();
mov ecx,edi ;move "this" pointer into ecx
mov eax,dword ptr [ecx] ;move "TypeHandle" into eax
mov eax,dword ptr [eax+0Ch] ;move IVMap address into eax at offset 12
mov eax,dword ptr [eax+30h] ;move the ifc impl start slot into eax
call dword ptr [eax] ;call Method1
mc.Method1();
mov ecx,esi ;move "this" pointer into ecx
cmp dword ptr [ecx],ecx ;compare and set flags
call dword ptr ds:[009552D8h];directly call Method1
These disassemblies show that the direct call to MyClass's instance method does not use offset. The JIT compiler writes the address of the MethodDesc directly into the code. Interface-based dispatch happens through IVMap and requires a few extra instructions than the direct dispatch. One is used to fetch the address of the IVMap, and the other to fetch the start slot of the interface implementation within the Method SlotTable. Also, casting an object instance to an interface merely copies the this pointer to the target variable. In Figure 2, the statement "mi1 = mc;" uses a single instruction to copy the OBJECTREF in mc to mi1.
mc.Method3();
Mov ecx,esi ;move "this" pointer into ecx
Mov eax,dword ptr [ecx] ;acquire the MethodTable address
Call dword ptr [eax+44h] ;dispatch to the method at offset 0x44
Virtual dispatch always occurs through a fixed slot number, irrespective of the MethodTable pointer in a given implementation class (type) hierarchy. During the MethodTable layout, ClassLoader replaces the parent implementation with the overriding child implementation. As a result, method calls coded against the parent object get dispatched to the child object's implementation. The disassembly shows that the dispatch occurs through slot number 8 in the debugger memory window (as seen in Figure 10) as well as the DumpMT output.
Figure 13 shows only a few of the fields relevant to this discussion. Because we've omitted some fields in the layout, we have not really shown the offsets in this figure. EEClass has a circular reference to MethodTable. EEClass also points MethodDesc chunks allocated on HighFrequencyHeap of the default AppDomain. A reference to a list of FieldDesc objects allocated on the process heap provides field layout information during MethodTable construction. EEClass is allocated on the LowFrequencyHeap of the AppDomain so that the operating system can better perform page management of memory, thereby reducing the working set.
.gif)
!Name2EE C:\Working\test\ClrInternals\Sample1.exe MyClass
MethodTable: 009552a0
EEClass: 02ca3508
Name: MyClass
The first argument to Name2EE is the module name that can be obtained from DumpDomain command. Now that we have the address of the EEClass, we'll dump the EEClass itself:
!DumpClass 02ca3508
Class Name : MyClass, mdToken : 02000004, Parent Class : 02c4c3e4
ClassLoader : 00163ad8, Method Table : 009552a0, Vtable Slots : 8
Total Method Slots : a, NumInstanceFields: 0,
NumStaticFields: 2,FieldDesc*: 00955224
MT Field Offset Type Attr Value Name
009552a0 4000001 2c CLASS static 00a8198c str
009552a0 4000002 30 System.UInt32 static aaaaaaaa ui
Figure 13 and the DumpClass output look essentially the same. Metadata token (mdToken) represents the MyClass index in the memory mapped metadata tables of the module PE file, and the Parent class points to System.Object. Sibling Chain (Figure 13) shows that it is loaded as a result of the loading of the Program class.